

They are the only cranial nerves to pass through canals.Įach cranial nerve can be described as being sensory, motor or both. 2-optic and 12-hypoglossal) exit through a canal of the same name. Tip: Cranial nerves with the number 2 in them (e.g. Figure 2 - Superior view of the skull base showing the foramina and which cranial nerves pass through them. The cranial nerves are numbered by their location on the brainstem (superior to inferior, then medial to lateral) and the order of their exit from the cranium (anterior to posterior) (Figures 1 & 2). Anterior to the olive: hypoglossal (XII).Posterior to the olive: glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory (IX-XI).Pontine-medulla junction - abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear (VI-VIII).Midbrain-pontine junction - oculomotor (III).It has the longest intracranial length of all the cranial nerves. Midbrain - the trochlear nerve (IV) comes from the posterior side of the midbrain.They can arise from a specific part of the brainstem (midbrain, pons or medulla), or from a junction between two parts: Cranial nerves III - XII arise from the brainstem (Figure 1). The olfactory nerve (CN I) and optic nerve (CN II) originate from the cerebrum. There are twelve cranial nerves in total. In this article, we shall summarise the anatomy of the cranial nerves - their origin, course, and functions.

The names of the cranial nerves relate to their function and they are numerically identified in roman numerals (I-XII). The first two nerves (olfactory and optic) arise from the cerebrum, whereas the remaining ten emerge from the brainstem.
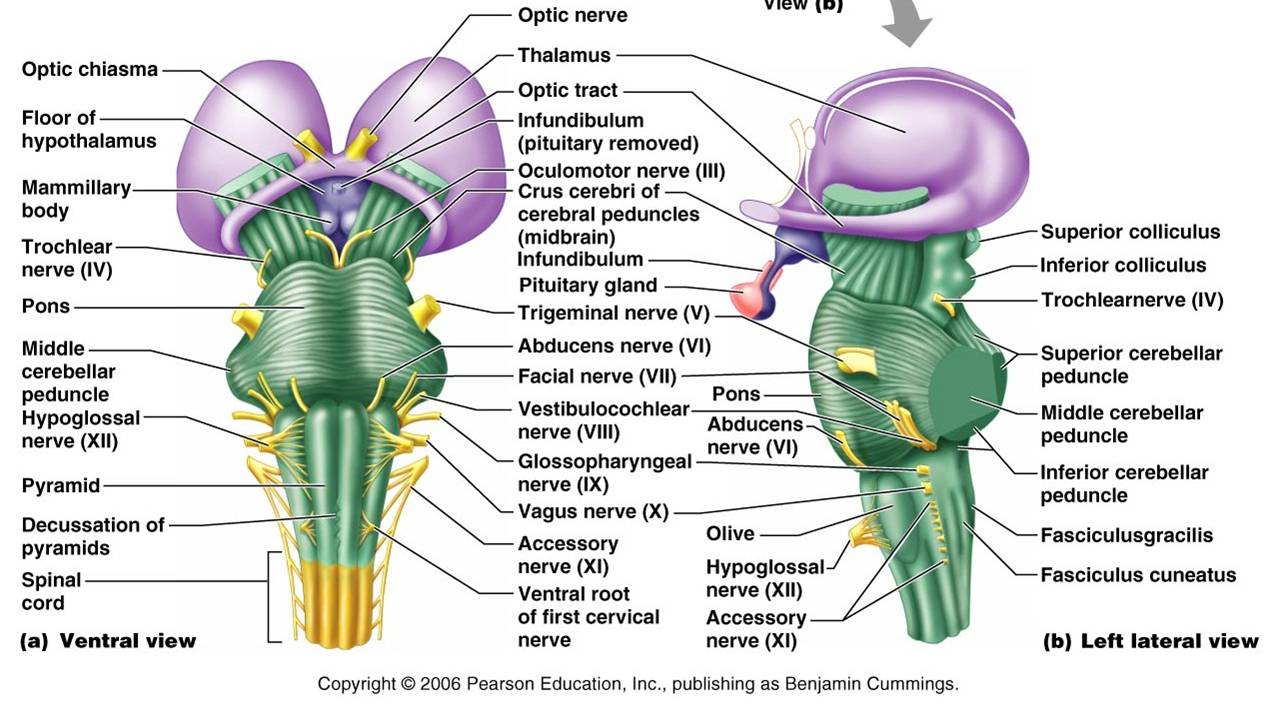
The cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves that arise directly from the brain. Intrinsic and extrinsic tongue muscles (except the palatoglossus). SVM: a few fibres run with CNX to viscera. GVM: smooth muscles of pharynx, larynx and most of the GIT. SVS: taste from epiglottis region of tongue GVS: larynx, pharynx and, thoracic & abdominal viscera. GVM: lacrimal, submandibular, sublingual glands and mucous glands of mouth and nose. Internal acoustic meatus > stylomastoid f.
Simple image brain stem function skin#
GSS: anterior 2/3 tongue, skin over mandible and lower teeth. GSM: 4 extrinsic eye muscles and levator palpebrae superioris.Ĭheeks, lower eye lid, nasal mucosa, upper lip, upper teeth and palate.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
